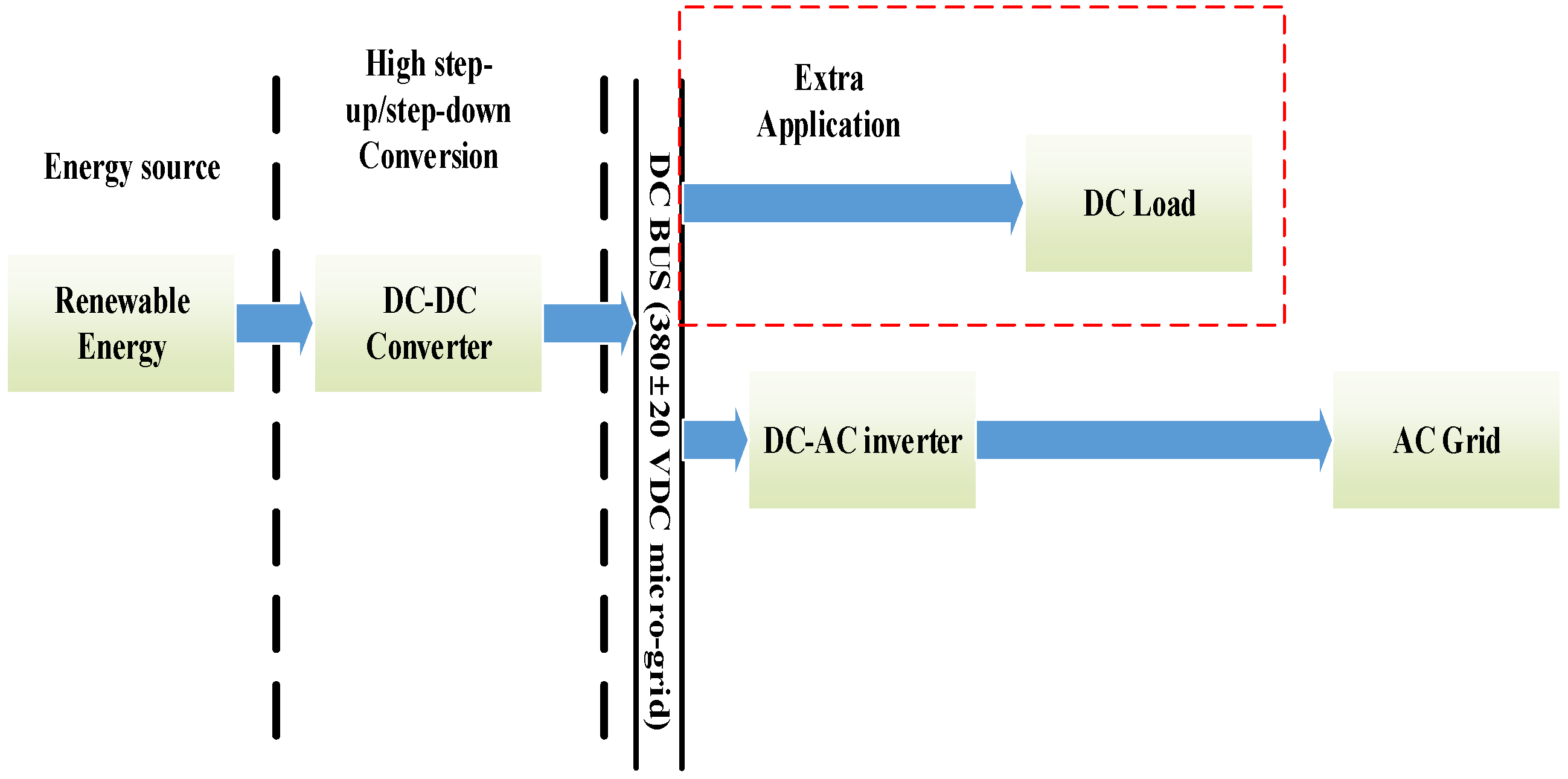
How to Simplify Power Design of DC Circuit Diagram This is particularly helpful in high-frequency, high-conversion ratio applications, because it allows for more precise control and minimizes the effect of delays due to other circuit elements. 2. The three-level buck converter in figure 3 was built to verify the design. The overall thickness of the circuit including the circuit board is only 5 mm. The circuit was tested with no forced air up to 12.5 A output current with a temperature rise of 65 °C. The switch-node voltage V SW waveform at 8 A output current is shown in figure 4.
Efficiency in a DC-DC Converter. There are many sources of loss in a DC-DC converter that reduce the efficiency of the system. These losses can be divided into two basic groups: efficiency losses caused by peak inductor current; and switching losses that occur each time that the circuit switches from charging to discharging phases. The 5kW Isolated Bidirectional DC -DC Converter reference design from Toshiba shows how to improve a power supply design's efficiency using SiC MOSFETs. The design uses the dual active bridge (DAB) method, one of the most popular topologies for such high-power converters. The DAB topology has full bridges on both sides, allowing the direction and

Calculating Efficiency (Rev. A) Circuit Diagram
Step 1: Set the Switching Frequency (R T). First, set the switching frequency with R T; the value chosen from Table 1 in the LT3999 data sheet.. R T = 12.1k sets f SW = 1MHz.. Step 2: Set the Input Voltage Range (UVLO, OVLO/DC) The UVLO (undervoltage lockout) and OVLO/DC (overvoltage lockout/ duty cycle) pins are used to set input voltage range.

Design of DC-DC Converters Frank Xi fxi@monolithicpower.com Monolithic Power Systems Inc. IEEE SSCS Dallas Chapter, October 2007. 11/1/2007 IEEE SSCS - Oct. 2007 2 High Efficiency at Light Load

DC Power Conversions and System Design Considerations for Battery ... Circuit Diagram
Designing a high efficiency DC-DC converter for these portable devices is challenging due to the special requirements of a battery operated system, such as a wide input voltage variation and dynamic operating load. The following sections, present the fundamentals and design considerations of various portable DC-DC